Best Practices Of Incident Management:
In the first part of our blog we explored the importance of automation in incident management,emphasising its advantages and difficulties.In this blog we will further understand about all the best practices which we can follow for an effective incident plan strategy.
We know that the unseen hero of IT operations and software development is incident response management. Effective incident response procedures operate in the background to make sure problems are fixed fast, allowing for uninterrupted performance, development, and communication.
In this blog We'll go over the benefits of cloud incident management and incident management best practices below so you can maintain the efficiency of your systems.
Overview of Cloud Incident Response:
An unanticipated disruption or decline in the quality of an IT service is referred to as an incident. In the modern world, businesses need to invest in a strong incident response management procedure to minimise security and business risks and avoid expensive downtime.
Conventional IT service management (ITSM) uses a variety of platforms and apps to track, monitor, and notify teams of issues as they arise.
IT workers must react to issues—and even foresee them—quickly and precisely as incidents have an impact on downtime, security, and performance. On the other hand, the current development teams of today require a velocity that classic ITSM just cannot match.
Transparency, teamwork, and quickness are essential for DevOps' smooth, speedy deployment. That is made possible by cloud incident response. All of these features—monitoring, communication, documentation, and alerting—are combined into a single, streamlined incident response solution with cloud incident response.Cloud incident response teams may now work together more effectively, monitor procedures, and automate important security duties.
Lets see what are the best practices which we need to follow for the Incident management
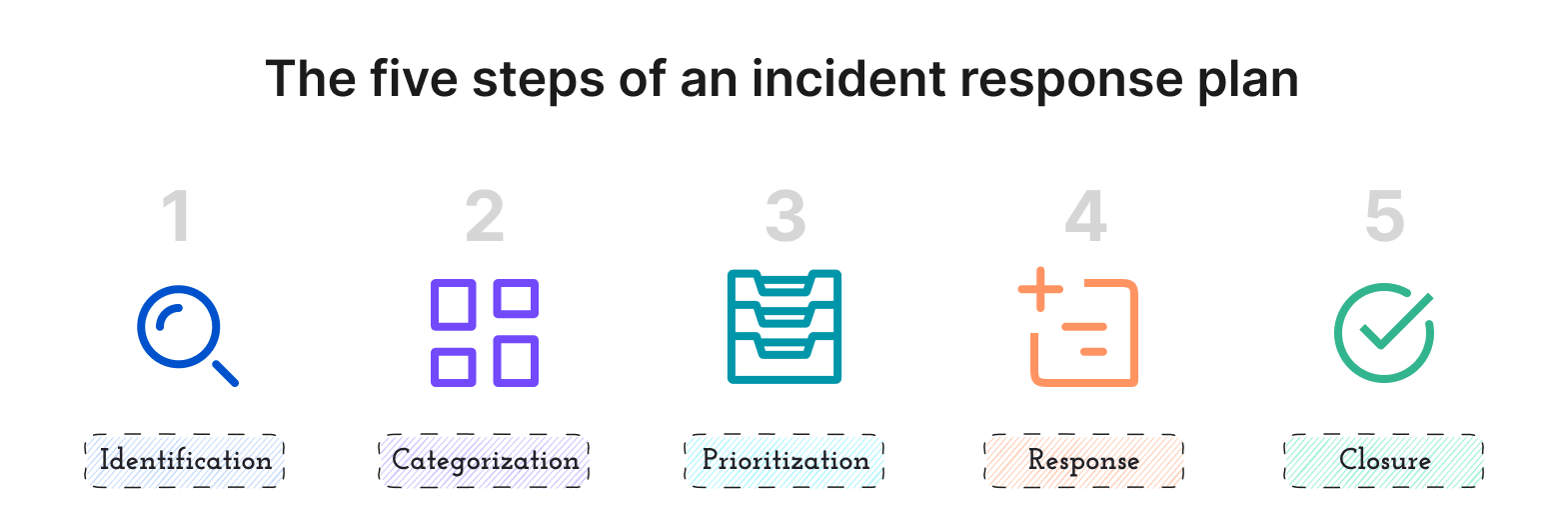
Best practices:
Cloud-based incident response has distinct requirements and presents its own set of obstacles despite the obvious benefits. To ensure that your problems don't worsen into crises, use these cloud incident response best practices.
1. Put a Process in place before the incident happens:
It is impossible to foresee every kind of event or incident that may arise and require your attention.Provide playbooks outlining the accepted practices for handling incidents. One advantage of an incident response management procedure is:
- Faster incident resolution
- Enhance communication both internally and outside.
- Cut down on revenue declines
- Encourage ongoing development and learning
- Provide a script that your team may use to inform stakeholders and customers about important outages. A team member's access to the training guides and the constant updating of your processes (automated if possible) should be ensured.
Establishing a recovery strategy lowers the possibility of expensive misunderstandings and confusion by ensuring you are prepared to respond to events swiftly and decisively.
2. Calculate Impact and prioritise risks:
You must possess the ability to act quickly when you notice an occurrence. What's the matter? Which risks does it present? Which hazards require attention the most? To whom does it affect?
In order to eliminate risks and minimize business disruption, you will have to respond to these questions swiftly and under pressure.
Utilizing important monitoring systems, escalation and diagnosis procedures, evaluate effects, and rank risks to decide how to respond. As well as well defined expectations for duty, make sure that all team members have open lines of communication.
So that incident managers can swiftly evaluate and decide priorities in the heat of the moment, and define your priority and severity levels in advance of an issue occurring. Prioritize resolving any upcoming incidents.

3. Invest in right tools:
Cloud architectures frequently have a lot of moving components that need to be tracked and monitored. To help your cloud incident response procedures, it is crucial to invest in the appropriate incident management technologies.
When possible, automate. This includes any monotonous, repetitive work that consumes significant time and energy. Employ automation to remove extraneous distractions from incident managers' workspaces so that everyone can concentrate on the most crucial tasks at hand.
Tools like Onepane helps you in capturing alerts, events, changes, and more from various sources, presenting a unified view of the incident and also analyses this consolidated data to identify potential correlations between changes and the incident, accelerating root cause identification.
4. OverCommunicate:
There's no such thing as too much communication in incident response. To make sure that everyone is in agreement, make use of your process flows, communications scripts, and incident response playbooks.
Documentation should be clear. Record each incidence and classify it. Usually, each ticket should contain:
- The individual's name who filed the incident report
- Time and date of the report
- Synopsis of the incident (what's broken)
- An exclusive ID to follow up on that incident
- Take into consideration setting up a status page to keep track of issue updates if you need to communicate with a sizable internal group.
Incident management involves a lot of moving components. Roles, responsibilities, communication routes, and expected processes should all be clearly mapped out to facilitate communication and reduce the possibility of anything getting lost in the process.
5. Host a Postmortem:
Continuous improvement is a culture that is essential to cloud incident response. After every incident, perform a postmortem.
Keep track of and evaluate events in a single database to determine what went wrong, how it was fixed, and the outcome of each incident. Monitoring and evaluating event data over time can enable you to detect trends or vulnerabilities in your infrastructure that require attention, as well as better prepare for future occurrences.
All these best practices must be followed in every organization to mitigate incidents whenever they happen.

